Date: September, 2017 | Category: Quality | Author: Marvin Magasura
Business owners and manufacturers know that flawed packages carry a negative message for their brands. An imperfect package is an imperfect business, especially living in a world with customers that have lofty expectations. A simple crooked label can transform people’s views of your brand and possibly change their purchasing decision forever.
Companies around the world place great value on packaging inspection. These quality control regimes must be set in motion in order to spot and reject printing errors, wrinkled labels, or crooked caps before they see the light of day.
Given the fast-paced packaging and manufacturing environment we live in, file comparison software is the ultimate tool that will quickly pay for itself by decreasing your business’ labor costs while also reducing liability due to complete recalls. More importantly, they are unflagging, communicative solutions that can adapt immediately to changing inspection parameters.
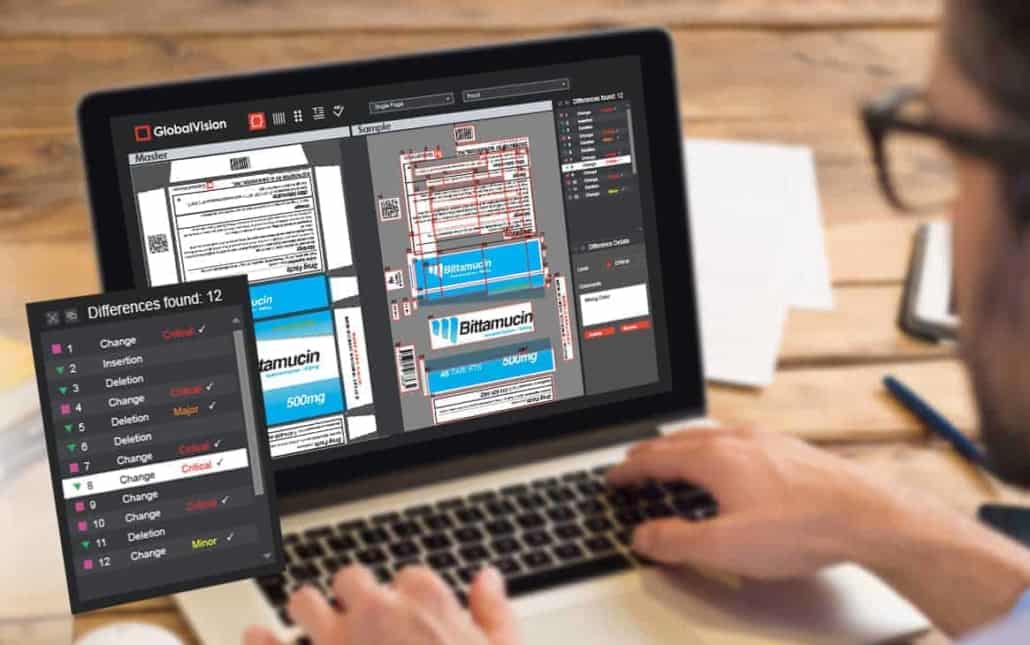
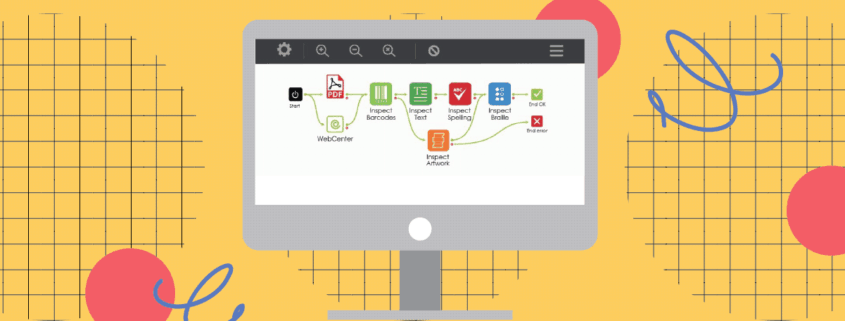
What makes file comparison software so effective is the technology and algorithms that allow them to “see” products and inspect them for flaws – all done at high-speed, with near-perfect accuracy. The brain of this solution is the analytic software in charge of processing what the software captures, and comparing it to the stored “ideal” file.
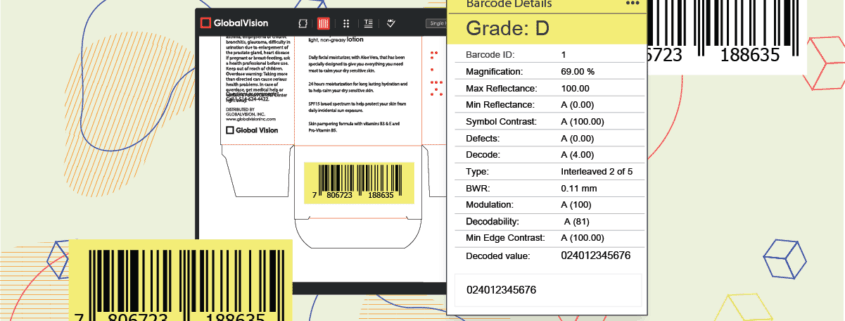
Today’s file comparison technology and other automated systems are so advanced that these solutions can quickly and accurately tally every item, contrast them with ideal images, point to printing errors, and verify barcodes in a matter of seconds.
However, one of the biggest benefits provided by these systems is user isolation. Users don’t need to understand its complex algorithms in order to use them. Through their HMI (human-machine interface), users just have to choose their inspection target, set the parameters, and press “Go”.

File Comparison Software for Complete Packaging Inspection
Besides letting you inspect packaging and products more easily, modern file comparison software can also proof and verify barcodes, alphanumeric codes, and data matrix images.
If you need it, these systems will also check the quality of incoming materials and ensure all steps and processes are done correctly. They can even take care of the quality of your pallet loads before shipping them to a customer. Therefore, because of this complete integration, your whole packaging line will be optimized.
In addition to the increase in inspection accuracy, which will boost your presence in the market, file comparison software can communicate with your business’s computer system and update your production, inventory, and maintenance records. It also provides reports on the total flaws detected. So, if these are higher than your threshold, it will shut down your entire production line until you make the necessary adjustments.
Of course, this level of efficiency in packaging automation varies depending on your needs and the amount of money you wish to invest. The market is filled with different systems that offer a wide arrange of features, from the described above to mere label inspections or barcode reading from the run sheet of the day. The best part is that the majority of them are quite adaptive; You can accommodate them to new products that require different parameters and adjustments.
Key Advantages
User-Friendly
Most, once installed, are very easy to use and require minimal maintenance.
Tech Support
Reputable file comparison software providers usually offer training programs for operators and ensure technical support in case anything goes wrong.
Market Diversity
The current file comparison software market provides a wide range of alternatives, meaning you can choose whichever best fits your needs.
Adaptability
Less-sophisticated solutions do not offer the ability to automate inspection changeovers, but modern high-tech systems can. So, if you run a diverse packaging line with a large variety of products, you can rest assured that you won’t be losing time doing manual changes every time a new product comes along.
The Cost of File Comparison Software
Like any new technology, especially when it comes to file comparison software, a certain initial investment is required. The actual amount depends on many elements, the main one being system complexity. File comparison technology ranges from a simple cloud-based application to physical scanners that use lights, cameras, lenses, and many other parts like servo motors and conveyors that allow for system adjustment to different targets, shapes, and sizes.
However, keep in mind that with any new investment, the words “cost” and “value” don’t mean the same thing. Focusing only on the financial expense of these systems will skew your assessment. Any prospective buyer of a file comparison software needs to weigh in a variety of factors:
● What are the system’s benefits/ features?
● Will I have to rearrange my entire production line?
● Does the software allow for simple in-house modifications in case any new product has to be checked?
● Do I get technical support from the manufacturer?
Add everything up and you’ll get the rough amount you need to spend. Now it’s time to include the prospective savings into the equation:
● Will I have to reduce the number of inspectors and operators?
● If so, will I reassign them to other areas?
● How much will automated packaging inspection boost my productivity?
And, most importantly, but often ignored:
● What will be my company’s financial value be if I get rid of customer complaints and complete recalls due to packaging mislabeling?
One word of advice before you make any decision: Erase any preconceived ideas from your mind. High technology is no longer a luxury that only big companies can obtain. File comparison software has evolved and the market is full of different choices, making packaging automation a gold standard and sophisticated practice available for small and medium companies alike.
Return on Investment for File Comparison Software
Due to the market’s wide diversification, prospective buyers now have a lot to evaluate. Every company considering crossing over to file comparison software should contemplate the implementation costs and possible completeness of their power supply along with its capability to adapt to new products and materials.
In addition, these systems typically provide quick ROIs, mostly because you’ll cut down on staff for manual inspection, not to mention all the savings related to fewer product recalls and fines from delivering flawed products.
Cutting down on staff is a tangible action. Therefore, you’ll get immediate results on your ROI. Decreasing fines and complete recalls are a lot harder to estimate accurately because the incidence of these events usually varies depending on the company, though. As a result, they usually are not considered at all when calculating the ROI for file comparison software. In spite of this, always keep in mind that, in the long run, these intangible forces can positively enhance your brand’s reputation and boost your profits.
The Future of File Comparison Software
In the future, file comparison software will probably advance in several areas. Current trends are drifting towards cost-efficient solutions suitable for all types of companies, but especially for packaging inspection. Advances will include, among others, a boost in system flexibility, an increase in smart technology, and greater software and hardware alternatives.
Just a few years ago we saw how smart cameras began to challenge PC-based vision systems by getting rid of the need for a separate processor. Although they’ve been available for over 20 years, they only just recently became small and affordable enough to justify an investment.
The quality of image sensors is getting better every year too. So, camera manufacturers are spending less time dealing with these types of defects and more on image processing. With the rise of complementary metal-oxide-semiconductors (CMOS), image sensors are also getting smaller, leaving room for developing further processing features, like color-processing, digital zoom, image enhancement, rotation, and much more.
With such high levels of integration and processing capacity, this all-in-one technology was once an emerging trend but now has started to dominate in the market. We are likely to witness more evolution of smart technology in the years to come.
When it comes to the packaging industry, advances in user-friendliness are likely to simplify the setup and usage of these systems even more. Ease of use will no longer imply a point-and-click graphical user interface, but a comprehensive approach with access to all features.
Less training will be needed and people with very different skill sets will be working with these machines, eliminating the need for time-consuming and pricey training programs.
Although prospective users might want to wait for what the future holds, the current file comparison technology developments mentioned throughout this article imply that the future is now. It’s an exciting time, and one for manufacturers and packaging companies to jump on board with packaging inspection automation.
File Comparision Software for Packaging
GlobalVision also has a wide range of packaging scanners available to suit different packaging line needs. They include non-contact scanners for wet-ink press sheets to cylindrical scanners for cans, jars, bottles, and any other type of cylindrical container.
Above all else, GlobalVision offers its Print Inspection tool, which allows for file comparison of printed packaging vs. approved digital artwork. This tool is the perfect solution to avoid reprints and reworks of any kind, due to printing errors like blemishes, smudges, and unwanted marks in general.
Learn More about Quality Management System
Get our guide to learn more about how to stay FDA-compliant with regulatory labeling obligations
Learn how some of the world’s top pharma companies have cracked the efficiency code with automation