Date: October, 2023 | Category: Compliance | Author: Hana Trokic
In the digital age, where data serves as the backbone of decision-making, business operations, and technological advancements, ensuring the integrity of data has become paramount.
From sensitive information to critical corporate records and beyond, the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data play a pivotal role in building trust, driving innovation, and avoiding potentially catastrophic consequences.
This comprehensive guide is designed to unravel the intricate layers of data integrity, offering insights into its significance, the challenges it poses, and, most importantly, the proven strategies and best practices that individuals and organizations can adopt to safeguard their data.
Whether you’re seeking to refine your enterprise’s practices, you’re a small company that is eager to improve its systems and security, or personally looking into how you can secure your data and privacy, this guide is your compass in navigating the complex landscape of data integrity assurance.
What is Data Integrity?
At its core, data integrity represents the steadfast accuracy and consistency of information throughout its lifecycle. It encompasses the assurance that data can be either valid, invalid or in the process of becoming valid.
Error-checking and validation processes are methods often used to ensure data integrity and it’s easier to think of it as the trustworthiness of a digital asset, where any modifications, corruptions, or unauthorized changes are effectively prevented or quickly detected and corrected.
In essence, data integrity is the pillar on which sound decision-making, seamless processes, and reliable systems are built. It not only guards against accidental errors and technical glitches but also shields against intentional tampering, ensuring that data retains its value and authenticity, fostering confidence among stakeholders and enabling a strong foundation for operational excellence.
The key to a successful software development lifecycle? Data integrity. Read more here!
Why is Data Integrity Important?
Data integrity is a cornerstone of modern information-driven landscapes, playing a pivotal role in upholding the credibility and effectiveness of any data-driven endeavor.
In a world where organizations and individuals rely on data for critical decision-making, strategic planning, and innovation, the importance of data integrity cannot be overstated.
Maintaining data in its accurate, unaltered state ensures that insights drawn and actions taken are based on a foundation of truth, enhancing the reliability of outcomes. Moreover, data integrity is a foundation of regulatory compliance, particularly in industries handling sensitive information such as healthcare and finance, for example.
Without robust data integrity measures, the risk of errors slipping through, compromised security, and a damaged brand image pose a large threat. By creating a culture of data integrity, organizations foster trust among stakeholders and customers while driving efficiency in operations and securing their ability to navigate the complexities of the digital age with confidence.
Data Integrity Best Practices
When it comes to ensuring data integrity, there are several fundamental principles that serve as the foundation for maintaining the reliability and trustworthiness of your data.
These principles are collectively known as ALCOA, an acronym that stands for Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate.
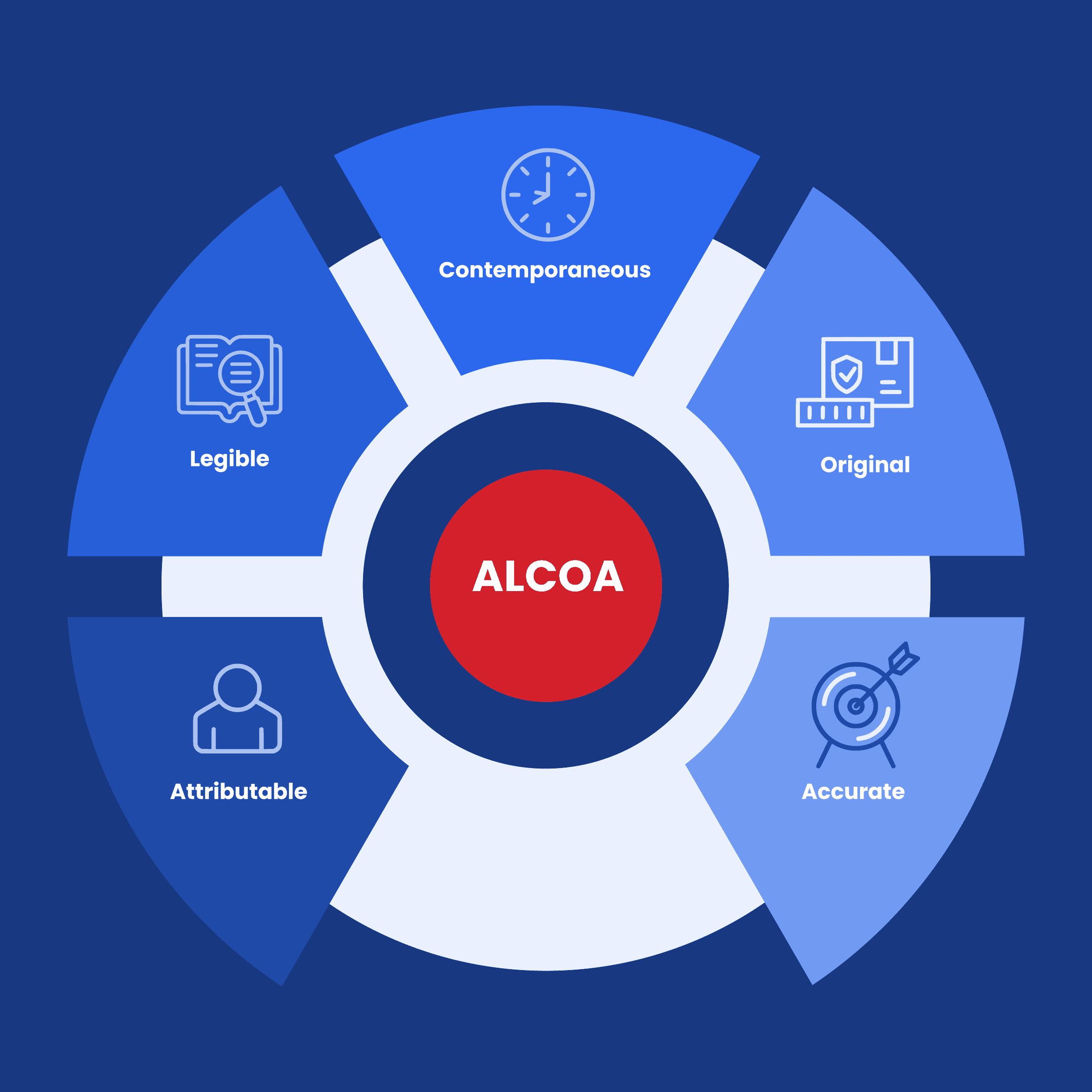
- Attributable: Data should clearly demonstrate who observed and recorded it when it was observed and recorded, and who it is about. This principle ensures transparency and accountability in data collection and management. When data is attributable, it becomes possible to trace its origins and understand the context in which it was generated.
- Legible: Data should be easy to understand and recorded permanently and original entries should be preserved. Legibility is crucial because it ensures that data can be effectively reviewed, analyzed, and shared without ambiguity.
- Contemporaneous: Data should be recorded as it was observed, and at the time it was executed. Timeliness in data recording is essential to prevent inaccuracies or omissions that can occur when data is retroactively documented.
- Original: Source data should be accessible and preserved in its original form. This ensures that data remains unaltered and unmanipulated throughout its lifecycle. Original data serves as a reference point for audits, validations, and quality assessments.
- Accurate: Data should be free from errors, and conform with the protocol. Accuracy is at the core of data integrity, as incorrect data can lead to faulty decisions, jeopardizing product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
What Are Threats to Data Integrity?
The landscape of data integrity faces a multitude of threats that can compromise the accuracy, reliability, and trustworthiness of information. Malicious cyberattacks, ranging from hacking and phishing to ransomware, pose a significant danger by potentially altering or stealing data.
System glitches, hardware failures, and software bugs can inadvertently introduce errors and inconsistencies. Data entry mistakes, often attributed to human error, can distort information at the point of creation.
Additionally, as data travels through various stages of its lifecycle, data integrity risks emerge during storage, transmission, and processing. Moreover, inadequate data governance and insufficient security measures can create vulnerabilities that malicious actors exploit. 
These threats collectively highlight the necessity of robust data integrity measures that encompass technological safeguards, employee training, vigilant monitoring, and stringent compliance with established protocols.
Overall, threats to data integrity can appear in many different forms. Some of the most common threats, however, are often internal. Examples include:
- Human error
- Unintended actions
- Security errors
- Malware
- Compromised hardware
How to Minimize Data Integrity Risks
In today’s marketplace, individuals and companies need to feel confident that there is no loss of quality when using computer systems. To accomplish this, there are effective strategies that companies may implement to manage their data integrity risks and ensure their data respects the ALCOA principle. By moving from a reactive to a proactive way of thinking, the following key requirements and controls may be put in place to ensure data integrity and minimize risks.
For more information about how you or your organization can ensure complete data integrity, read our detailed blog post.
Top Backup Strategies to Keep Data Integrity Intact
Just backing up data isn’t enough to keep data intact anymore. While it’s a necessary step and a good start, a backup means little if there aren’t adequate safeguards in place to protect the integrity of the data that might have to be recovered.
Even if backups themselves are a safeguard, they must be seen as an asset in their own right. After all, it’s estimated that 100 MB of company data is worth $1 million on average. Half the firms that cannot recover lost data in 10 days cannot recover themselves.
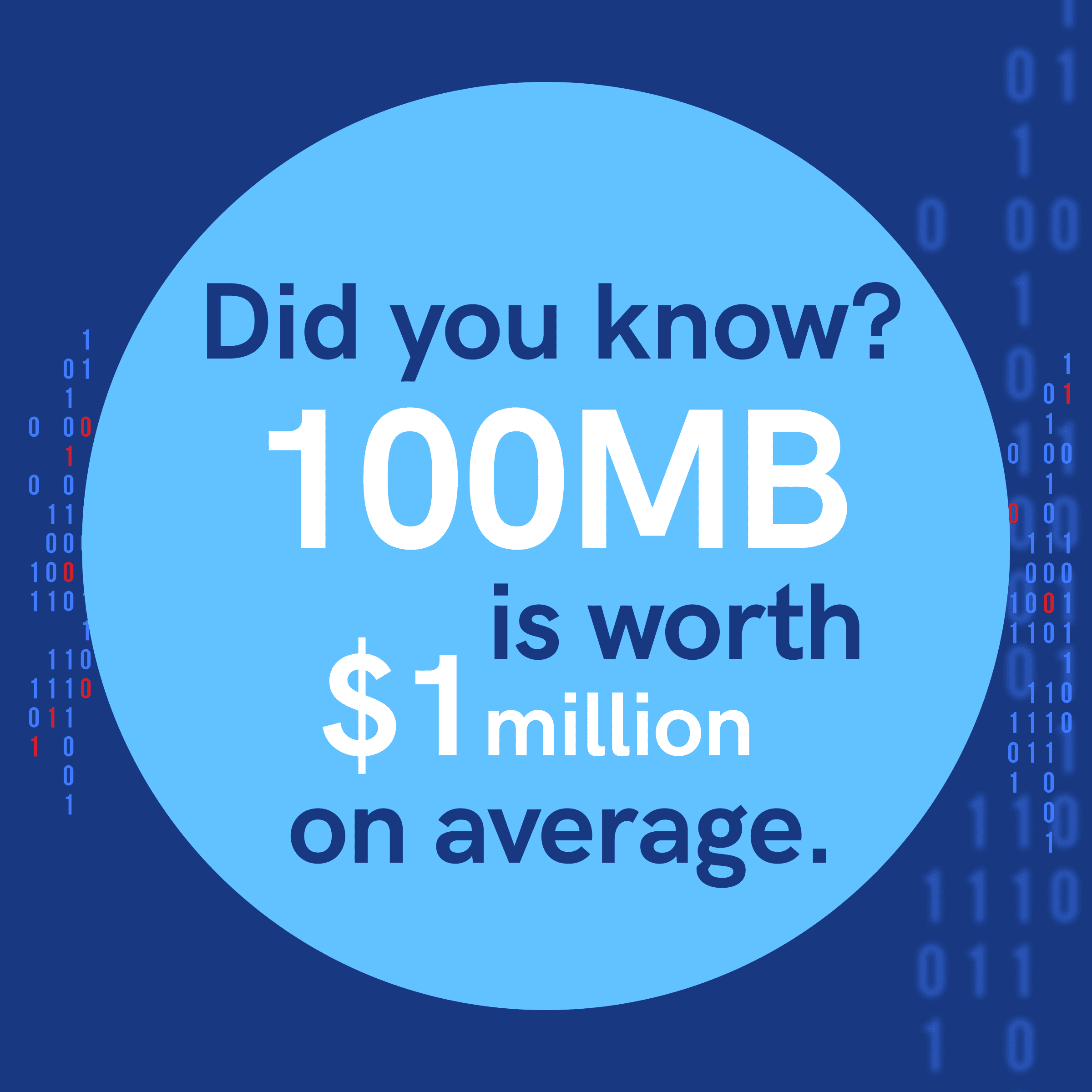
That is why, it is in every individual’s and company’s interest to have a good backup plan and strategy in place. Here are some backup strategies to keep data intact:
- Know What to Back Up: It’s not only files that must be backed up but programs, including Operating System software as well.
- Encrypt Your Back-Ups: Information must be kept secure for its data integrity to stay intact. One way to avoid confidential information from being compromised is to encrypt it into code.
- Make Regular Back-Ups: Ideally scheduled for when there is low network activity to prevent slowdown, back-ups should be made every day, with daily snapshots taken as well to monitor performance.
- Store Your Back-Ups Properly: It goes beyond storing your backups in environmentally controlled facilities. You would also want to store your backups off-site, separately from the original data.
- Validate the Recovery Procedure: Validation can take many forms from Installation, Operational, and Performance Qualification procedures to verify the application works as it should.
To find out more about best practices and top-back-up strategies to keep your data integrity intact, read our in-depth blog post.
How to Reduce Data Integrity Risks for Regulated Industries
In regulated industries, reducing data integrity risks is paramount to ensure compliance and maintain public trust. By implementing stringent data management protocols, conducting regular audits, and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability, organizations can effectively mitigate data integrity risks and uphold regulatory standards.
Here are some ways businesses in regulated industries can overcome data integrity issues:
- Validate Input: Documented evidence of validation is a crucial way to ensure that input data is accurate. Once a data set is received, it should always be systematically verified.
- Validate Data: Ensuring data meets pre-determined specifications and key attributes is crucial to ensuring its validity and the system through which it passes.
- Remove Unnecessary Data: Duplicate files and unidentified data can potentially open doors to unwanted intruders set on exploiting or corrupting information.
- Data Back-Ups: Permanent data loss is a real threat to businesses. Staying on top of routine backup checks is crucial to avoid losing critical information. Businesses should be proactive in creating a recovery strategy in the event of an unexpected data loss or application error. This will help to restore any losses that could potentially occur.
- Manage Access Control: Setting limits and controls on who can access certain information within an organization is crucial in protecting data from unauthorized users, including intruders and impersonators. Actions must be taken to ensure that the unwanted spread of sensitive information is limited. Furthermore, the importance of physical access controls must not be neglected. Businesses should take care to protect places like server rooms that can be especially vulnerable to corruption.
- Traceability: Data integrity relies heavily on the ability to track down the source of a breach at any point within operations. Ensuring that audit trails are consistently in place helps to provide security in the event of a breach and allows organizations to identify the source.
For a step-by-step look at how you or your organization can ensure data integrity, read our in-depth “12 Ways to Reduce Data Integrity Risks for Regulated Industries”
The Role of Document Comparison Software in Ensuring Data Integrity
As automation technology becomes increasingly prevalent and the use of different software, applications, and the internet becomes an absolute necessity, data integrity is as important as ever. Not only does it serve as the driving force behind technology of all forms, but it also acts as a fail-safe.
Document comparison software is one viable way to catch and stop errors that risk corrupting data in their tracks. The software is designed to compare two or more documents to identify all differences, changes, and errors between them allowing for ease of proofreading, and editing and ultimately leading to error-free content. As previously mentioned, this type of software is particularly useful in industries that deal with highly regulated and critical content.
Here are some ways document comparison software can help ensure data integrity:
- Enhances security
- Reduces Human Error
- Prevents Issues from Recurring
Enhances Security
While data security is different than data integrity, the two go hand in hand. Like data quality, data security is a single facet of data integrity (but not vice versa). Nevertheless, without the proper degree of security, data can become compromised due to breaches, among other threats. In other words, for data to have integrity, it must first be secure.
As a result, document comparison software can be considered a key component of any complement of tools designed and implemented to enhance the security of data. Errors are simply outliers or anomalies, which are defined as observations that lie outside of norms Document comparison software can build baselines of systems, their users, and the data they create, leading to the easy detection of behavioral deviations, whether there is malicious intent or not.
Do you think following FDA data integrity guidelines is hard? It’s way easier than you think!
Reduces Human Error
There’s an inherent risk whenever you rely on human resources. There are some things a machine will likely never be able to do as well, but analyzing data is not one of them. It’s similar to the situation with manual proofreading, where, the longer the process is, the less likely errors are to get caught. Fatigue sets in eventually and the effectiveness of proofreaders declines over time.
In much the same way, the automated analysis of unstructured data saves time, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the process. Employees wouldn’t be replaced, either. There would still be a need to oversee the analysis. The right document comparison software would all the while keep relevant parties apprised of how the data behaves.
Interested in learning more about how document comparison software can help ensure data integrity? Read more here!
Prevents Issues from Recurring
It isn’t just the current errors the software might catch, but the ones in the future that would otherwise slip through the cracks. Consider document comparison software as an example. A form of error-detection software, GlobalVision features an audit trail for compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
The platform doesn’t just go over the document pixel-by-pixel or character-by-character to detect graphics and text differences (among other types). The application tracks parameter changes and log-ins, so data becomes “attributable,” one of the five principles of data integrity.
Read about how GlobalVision Adds Electronic Signatures for Enhanced Data Integrity to the Most Comprehensive Platform Yet!
The Importance of an Audit Trail to Securing Data Integrity
Though the word might spring negative connotations, audits are an unavoidable part of life for many corporations that bring many benefits to daily functions and processes.
In essence, trails are the lists of transactions or events kept track of to help auditors and, in many ways, those being audited as well. An audit is simply an investigation of accounts and records in general.
For example, audits can be key to achieving and maintaining regulatory compliance, which is in turn critical to operating in regulatory sectors. It is also important to note that external and internal audits are to be expected on a regular basis.
External vs. Internal Audits
External audits and internal audits serve different purposes:
- External audits: done by independent third parties and focused on confirming accurate financial statements for regulators and stakeholders.
- Internal audits: performed by the organization’s own team, and aims to assess and improve internal controls, risk management, operations, and adherence to policies.
The Benefits of an Audit Trail
Regardless of the focus of an audit, trials are undeniably critical to their success. And success is what all parties should strive for, whether they’re doing the auditing or being audited.

Audits can be made easier if all required records have been kept and are easily accessible to auditors. Automated trails that are easily searchable make smooth audits more of a reality.
Trails are theoretically included in the software as one of many required technical controls that enable users to achieve compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 with the Food and Drug Administration (in the United States; equivalent to Annex 11 in the European Union).
Compliance here ensures companies implement good business practices through reliable electronic records, which must be able to be accurately displayed and exported. Here, the audit trail serves to log what changes to application data were made, when, and by whom and be available for review.
Whoever ends up conducting that review, whether it’s an agency or the company itself, the auditor will no doubt thank you as the bigger picture begins to take shape. Identifying the individual trees is key to seeing the forest as a whole, though. Finding your way through can be hard, but an audit trail can clearly reveal the right path to take.
Read more about the importance of an audit trail to securing data integrity here.
Step Up Your Data Security
Data integrity serves as the pillar for informed decision-making, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
By delving into the significance of data integrity, the principles of ALCOA, threats to data security, and practical strategies for safeguarding it, this guide equips individuals and organizations with the knowledge and tools necessary to protect their data assets.
Whether you are an individual seeking to secure your personal information or a business aiming to strengthen your operations and brand, the principles and practices outlined provide a compass to navigate the complexities of the digital age with confidence.
As data continues to evolve and become more integral to our lives, the assurance of its integrity remains vital, ensuring that our digital assets are built on strong foundations of truth, trust, and reliability.
Ready to upgrade your data security? Take a step in the right direction by setting up proper processes through automated quality control. Request a demo of our innovative proofreading software and see how this technology can revolutionize your everyday business practices along with your data security.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Did you enjoy reading this post? Check out these other related post:
- 6 Ways Businesses Can Overcome Data Integrity Issues
- The Top Back-Up Strategies to Keep Data Integrity Intact
- Logical System Security as Crucial to Data Integrity as Physical Measures
- 3 Ways Error-Detection Software Ensures Data Integrity
- The Key to a Successful Software Development Lifecycle? Data Integrity.
- The Importance of an Audit Trail to Securing Data Integrity
- 12 Ways to Reduce Data Integrity Risks for Regulated Industries
- Following FDA Data Integrity Guidelines Is Easier than You Think





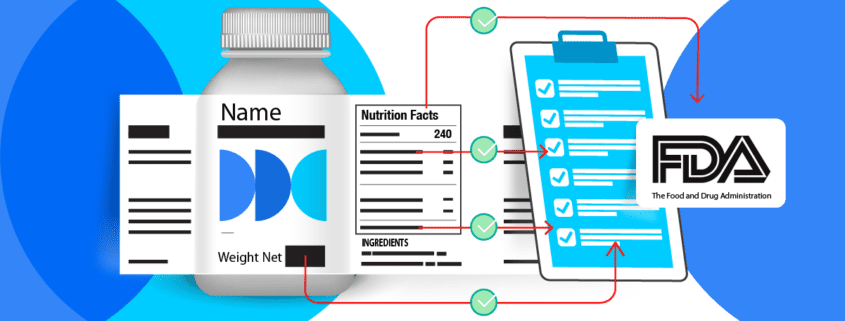








 Food labels are critical. Not only do they provide vital information to consumers about the food choices they are making, but they are also legally and governmentally mandated and regulated. Those labels we see and read daily are crucial to ensuring the health and safety of the general public and consumer.
Food labels are critical. Not only do they provide vital information to consumers about the food choices they are making, but they are also legally and governmentally mandated and regulated. Those labels we see and read daily are crucial to ensuring the health and safety of the general public and consumer.




 If you want to keep up with FDA drug labeling requirements with complete ease, switch to automated quality control. A trusted technology,
If you want to keep up with FDA drug labeling requirements with complete ease, switch to automated quality control. A trusted technology,