Date: April, 2016 | Category: Compliance | Author: Reuben Malz
No matter what industry you are in there are always new regulations that impact the way you create labeling artwork. Staying compliant with regulatory labeling obligations is a complex undertaking that if done wrong may result in undesired errors or reworking.
Regulatory Label Compliance with GlobalVision
GlobalVision provides a Quality Control Platform to proofread artwork, text, print, barcode, and Braille and is designed to help you maintain regulatory compliance.
Major regulations now in place or planned are listed below along with an appropriate GlobalVision solution that can enhance the quality and speed of inspections:
Chemical
OSHA – Hazard Communication Standard (United States)
In order to ensure chemical safety in the workplace, information about the identities and hazards of the chemicals must be available to workers.
WHMIS 2015 – Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (Canada)
A regulation to provide health and safety information on hazardous products (labeling, safety data sheets) that is intended for use, handling, or storage in Canadian workplaces.
New Requirements
Chemical manufacturers and importers will be required to provide a label that includes a harmonized signal word, pictogram, and hazard statement for each hazard class and category. Precautionary statements must also be provided.
The GlobalVision Solution
GlobalVision Text Inspection Solution
- Validates that the correct font and text size are used on the label for artwork.
- Verifies that the correct font, size, and style are used to differentiate the Signal word
GlobalVision Graphics and Artwork Inspection Solution
- Verifies artwork including pictograms on a pixel-by-pixel basis.
Food
Food Labeling Modernization Act (Canada)
Update of food packaging labels designed to improve access to information and to increase awareness, to help consumers to make informed decisions about the food they buy.
EU Regulation 1169/2011 (European Union)
Revision of product information on product packaging and online stores pertaining to food and beverages sold in the EU. The objective of which is to standardize food labeling and provide greater clarity to consumers concerning ingredients, nutrition and allergens.
FDA Nutrition Fact Labels Revision (United States)
Update of food labels in the United States to reflect up-to-date serving sizes, as well as percent daily value, designed to better inform consumers.
ACC Country of Origin Labels (Australia)
Revision of food labels to include the addition of a statement and a bar graph indicating the proportion of Australian ingredients by weight.
New Requirements
New food labeling directives all specify lists of mandatory information and details on how the label information should be formatted and displayed – including minimum font requirements, new artwork, and tables on food packaging included in the new formats.
The GlobalVision Solution
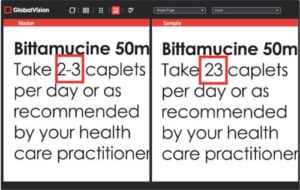
GlobalVision Text Inspection Solution
- Validates that the correct font and font size are used during typesetting. The font type and size have a direct correlation to the X-Height of the final printed package.
- Verifies that the correct font, size, and style were used to define different elements.
GlobalVision Graphics and Artwork Inspection Solution
- Compares previous artwork to new version artwork, to ensure stylistic differences are present.
GlobalVision Print Inspection Solution
- Inspects X-Height in mm on the final printed packaging.
- Compares the previous package to the new version of the package, to ensure stylistic differences are present.
GlobalVision Barcode inspection
- Verifies and grades the barcode to ensure accuracy and scanability.
Braille
ISO 17351:2013 (European Union)
Standard outlining the requirements and providing guidance for the application of Braille to the labeling of medicinal products.
Safety and Innovation Act (Pub. L. 112-144, 126 Stat. 993) (United States)
A series of best practices on how to offer guidance to pharmacies and provide accessible prescription drug container labels to patients with visual impairments to enable them to manage their medications independently and privately.
New Requirements
New Braille regulations require Braille on the outside packaging of all medication – including name, and dosage of medication.
The GlobalVision Solution
GlobalVision Braille Inspection Solution
- Ensures that Braille Dot Height meets the 0.20 mm requirements ensuring readability by visually impaired persons.
- Verifies the Braille character spacing
- Translates Braille into readable text
Pharmaceutical

Directive 2001/83/EC Article 11 (European Union)
Updated packaging and labeling regulations for the EU
FDA Opioid Action Plan (United States)
Revised labeling requirements is to better inform doctors about the risks of opioids and how to prescribe these drugs safely.
FDA NSAID Warning (United States)
Revised warning labels that non-aspirin non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may cause heart attacks or strokes
New Requirements
Packaging content must match the approved QRD template from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) (for EU).
Multiple modifications and additions to the packaging, labeling, warning labels, and associated literature.
The GlobalVision Solution
GlobalVision Text Inspection Solution
- Ensures that the approved content contained within the QRD template is consistent with the carton, folding boxes for medicinal products (for EU)
- Medical spell-check
- Complex table handling
- Detect deviations between packaging, labels, leaflets, and the text of the Annexes
GlobalVision Graphics and Artwork Inspection Solution
- Compares previous label artwork to new version artwork, to ensure stylistic differences are present.
For more information on the GlobalVision Quality Control Platform
and how it can help with your compliance requirements please visit globalvision.co
Journey of the Package Printing Process
Our helpful guide walks you through the major steps of a typical package printing process, and how you can ensure a flawless delivery, every time.